强化学习相关调研
青山无数,归去又还秋暮,算恁地光阴,能来得几度 —— 老俞
上半年论文计划 (2月~10月)
重点论文:面向强化学习/大模型的存储优化
- 目标会议:FAST (7月-9月)
DAC 论文转投 ICPP‘22 (4月9号),ASE’22 (4月29日)
公布了中奖号码,223 / 大约1418 = 15.72
- 添加:背景+相关工作(1页)+实验(3页)
IPDPS论文转投期刊 TPDS/TOC
- 五月开会
KV Scan:暂缓
面向强化学习的存储优化
XX: Efficient XX Storage Service for Reinforcement Learning Applications 或者Decision AI Applications
- 目标:FAST (7月-9月),
SC (3月25日),HPCA(7月),ASPLOS(8月),ISCA(11月);ATC(1月),OSDI (1月),SOSP(奇数年), DAC(12月), MICRO(不相干) - 当前困境:项目模式很难搞论文,和他们合作有点过于墨迹
- 当前进展:调研问题,测试瓶颈,寻找创新
- 我们有环境有机器,用他们的平台直接自己测试,寻找瓶颈
- 分布式强化学习的发展和优化,以及存储优化思考
Abstract
- 加速强化学习的统一对象存储服务 Di-store: Decision Intelligence Store
Introduce
Background and Motivation
- RL介绍和训练框架
- Replay Buffer
- 相关问题
Scalable/Distributed RL
- 并行算法:Ape-X,R2D2,IMPALA,A3C,G-A3C,SEED_RL,Agent57
- 环境的并行:这里特指单机条件下使用wrapper对环境进行封装,使得可以同时运行很多环境,打batch使用网络进行inference。当然这个其实不怎么算大规模,不过一般的Research我觉得可能环境并行就差不多了,上升不到真正的大规模
- Actor的并行:这里主要是值Ape-X、A3C等Scalable RL算法中的Actor,其作用主要是在每个机器/线程上运行一个Actor同若干数量的envs进行交互来收集数据
- Learner并行:这里主要是类似分布式深度学习,基于单机多卡或者多机多卡进行大batch的训练
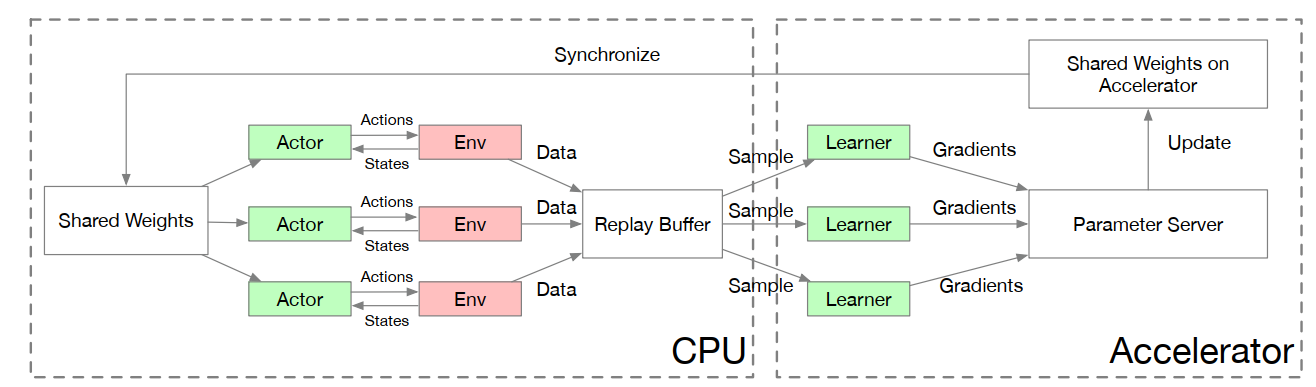
(A3C)Asynchronous Methods for Deep Reinforcement Learning,ICML‘16,DeepMind
- 系列:A2C,G-A3C(GPU版A3C)
(Ape-X)Distributed Prioritized Experience Replay,ICLR ‘18,DeepMind
IMPALA: Scalable Distributed Deep-RL with Importance Weighted Actor-Learner Architectures,ICML’18,DeepMind
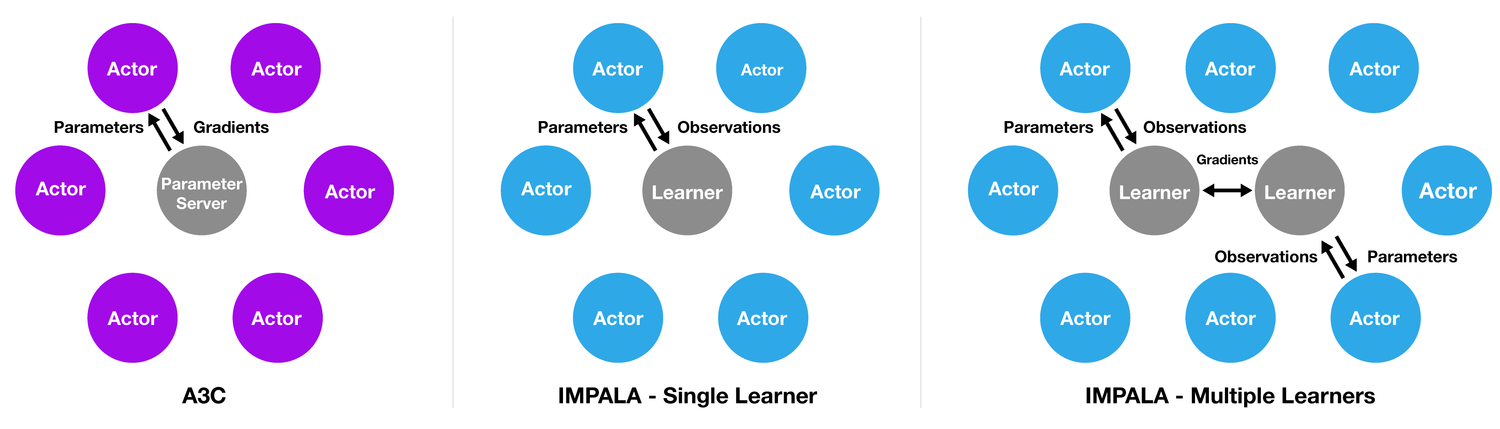
(R2D2)Recurrent Experience Replay in Distributed Reinforcement Learning,ICLR’19,DeepMind
- R2D2,Recurrent Replay Distributed DQN
- (R2D3)Recurrent Replay Distributed DQN from Demonstrations
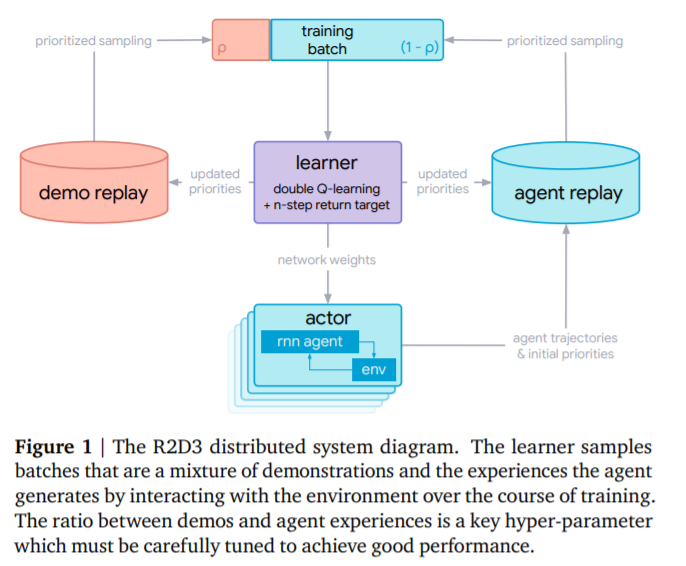
- Dota 2 with Large Scale Deep Reinforcement Learning,OpenAI
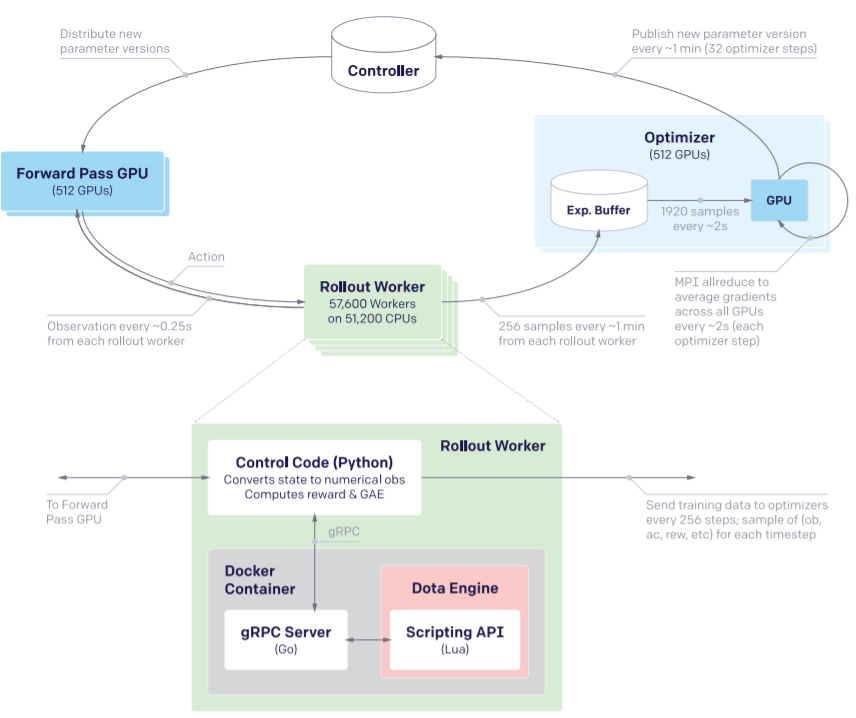
- SEED RL: Scalable and Efficient Deep-RL with Accelerated Central Inference,ICLR 2020,Google Research
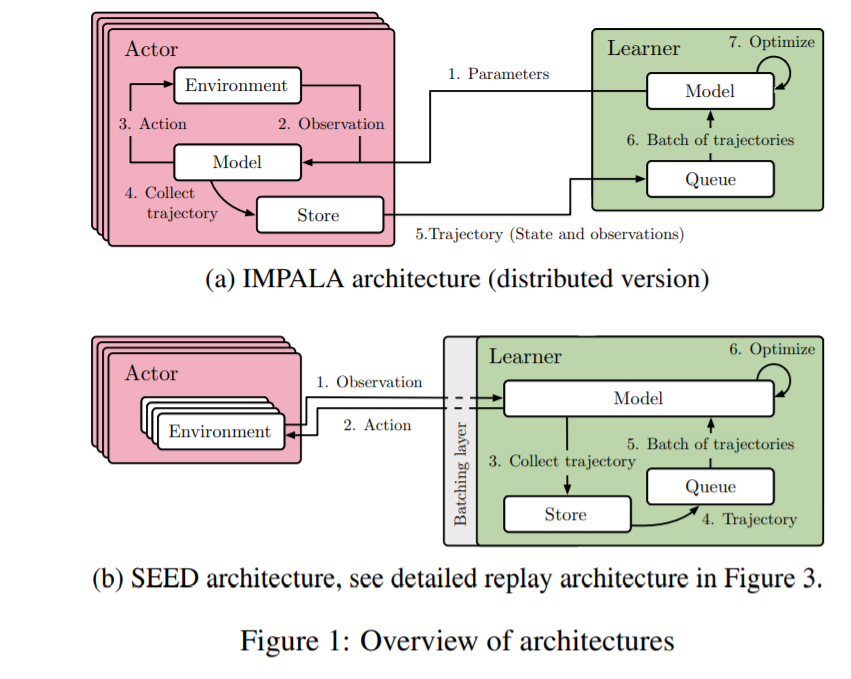
- Instead of a distributed replay buffer, we show that it is possible to keep the replay buffer on the learner with a straightforward flexible implementation. This reduces complexity by removing one type of job in the setup. It has the drawback of being limited by the memory of the learner but it was not a problem in our experiments by a large margin: a replay buffer of 105 trajectories of length 120 of 84 × 84 uncompressed grayscale observations (following R2D2’s hyperparameters) takes 85GBs of RAM, while Google Cloud machines can offer hundreds of GBs. However, nothing prevents the use of a distributed replay buffer together with SEED’s central inference, in cases where a much larger replay buffer is needed.
不适用一个分布式的replay buffer,我们表明它是可能的,以一个简单的灵活的实现在learner 上保持replay buffer。 这通过在设置中删除一种作业类型来降低复杂性。 它的缺点learner 内存限制,但它不是一个问题。105 trajectories 的replay buffer长度为120的84×84未压缩grayscale observations(根据R2D2 超参数)需要85 GB的内存,而谷歌云机器可以提供数以百计的GBs。 然而,在需要更大的重放缓冲区的情况下,没有什么可以阻止分布式replay buffer与SEED的中心推理一起使用。
Sample Factory: Egocentric 3D Control from Pixels at 100000 FPS with Asynchronous Reinforcement Learning
- ICML’20,Intel,南加大
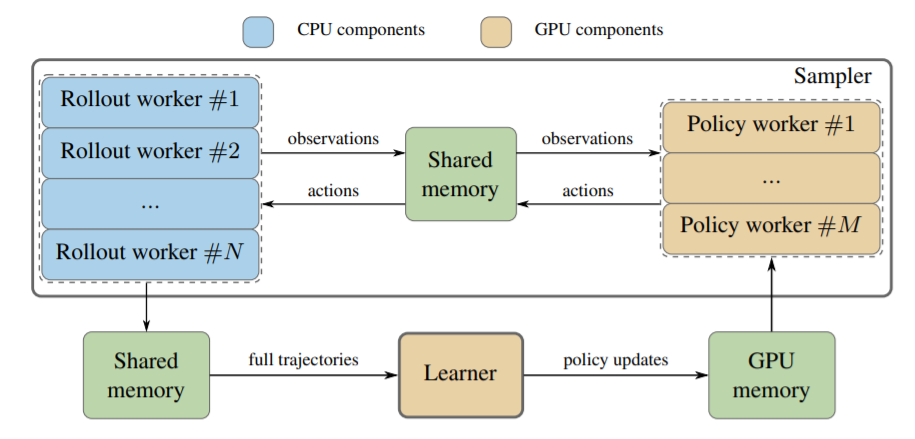
Acme: A Research Framework for Distributed Reinforcement Learning,DeepMind
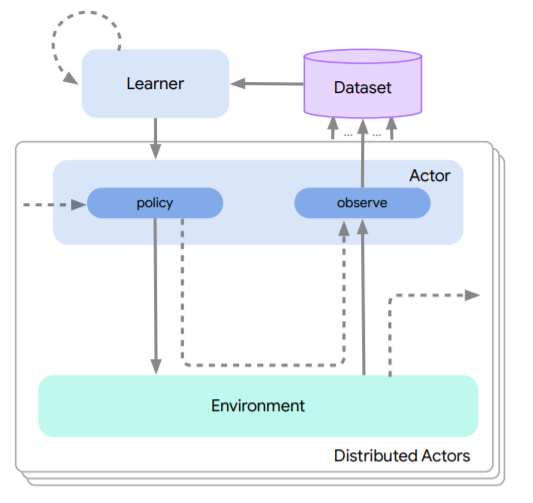
NGU && Agent57
Never Give Up: Learning Directed Exploration Strategies, ICLR‘20,Deepmind
Agent57: Outperforming the Atari Human Benchmark,ICML‘20,DeepMind
训练框架
- OpenAI的Baselines、SpinningUp;加州伯克利大学的开源分布式强化学习框架RLlib、rlpyt 、rlkit 、Garage;谷歌Deepmind的Dopamine、B-suite ;其他独立开发的平台Stable-Baselines、keras-rl、PyTorch-DRL、TensorForce、Tianshou、Di-engine
- 优化方式:multiple/parallel actors-learners,asynchronous actors-learners
- 分布式RL:DQN,GORILA,A3C,Ape-X,IMPALA,SEED_RL…
- Implicit Quantile Networks for Distributional Reinforcement Learning
- RLlib: Abstractions for Distributed Reinforcement Learning
- IMPALA: Scalable Distributed Deep-RL with Importance Weighted Actor-Learner Architectures
- 分布式RL:DQN,GORILA,A3C,Ape-X,IMPALA,SEED_RL…
论文—RLlib
RLlib: Abstractions for Distributed Reinforcement Learning,ICML‘18,伯克利
RLlib是开源项目Ray的一部分,RLlib官方文档,实现了自顶向下分层控制的强化学习算法
Replay Buffer
- 经验回放使得在线强化学习的agent能够记住和重新利用过去的经验,在以往的研究中,过去的经验(transition,经验池中的一条记录,表示为元组形式,包含state,action,reward,discount factor,next state)
- 关键问题:一是选择哪些经验进行存储,二是如何进行回放
论文——Prioritized Experience Replay
- 回放较为重要的经验,加快收敛
论文——Distributed Prioritized Experience Replay
论文——Parallel Actors and Learners: A Framework for Generating Scalable RL Implementations
问题
- 性能瓶颈
- 随着加速器硬件和高速网络发展,瓶颈在向存储转移 — 需要测试
- 目前都是并行训练 / 分布式训练架构,存储瓶颈更明显 — 需要测试
- 容量瓶颈
- 随着环境愈发复杂和算法的发展,模型/经验存储容量需求愈高
- 不同环境 / 算法replay buffer大小 — 需要测试
- 存储资源利用率低 — 需要测试
replay buffer存储需求
| 算法 | 环境 | Buffer大小 | Buffer特性 | Buffer中单个元素大小 | 添加数据的速度(个/s) | 添加数据的速度(Byte/s) | 取出(采样)数据的速度(个/s) | 取出(采样)数据的速度(Byte/s) | | ——– | ————- | ———- | ———————- | ——————– | ——————— | ———————— | —————————— | ——————————– | | DQN | Atari-Qbert | 40w | 需要定义数据采样优先级 | 110KB | 400个/s | 44MB/s | 1650个/s | 181MB/s | | PPO(off) | Atari-Qbert | 10w | 需要控制数据使用次数 | 120KB | 50个/s | 6MB/s | 87个/s | 10MB/s | | R2D2 | Atari-Qbert | 1w | 需要定义数据采样优先级 | 10MB | 3个/s | 30MB/s | 45个/s | 450MB/s | | IMPALA | Atari-Qbert | 10w | 需要控制数据使用次数 | 3MB | 4个/s | 12MB/s | 253个/s | 759MB/s | | SAC | Mujoco-hopper | 100w | 无 | 3KB | 71个/s | 213KB/s | 138个/s | 16MB/s | | QMIX | SMAC-3s5z | 5w | 无 | 290KB | 19个/s | 6MB/s | 60个/s | 17MB/s | | MASAC | SMAC-3s5z | 100w | 无 | 29KB | 116个/s | 3MB/s | 63个/s | 2MB/s | | DQN | GoBigger | 10w | 需要定义数据采样优先级 | 400KB | 30个/s | 12MB/s | 83个/s | 33MB/s |
- 最大是R2D2,IMPALA:100,300GB
测试
基于A100 Ray/DI-engine训练测试:doing
Replay buffer大小测试:doing
Design
对标:ray-内存object store,NoPFS-预取加速IO,CacheLib,…
- 性能:高性能存储服务,分布式架构(一致性和容错支持),支持高性能网络、共享内存、prefetch…
- 容量:统一资源管理(CPU-memory,NVMe ssd…),大容量,提供offload机制…
Evaluation
Others
大模型
- 训练效率问题:暂不考虑
- 内存限制问题
- checkpoint效率问题
buffer问题:
- buffer大小是策略一开始就确定的嘛 还是会动态扩增
- buffer大小和什么有关?
- buffer大小对性能、精度的影响
